Gluconeogenesis (abbreviated as GNG) is a complex metabolic process which takes place mainly in the liver and to a lesser extent in the kidneys. GNG is responsible generating glucose from other, non-carbohydrate substrates such as protein, lactate, glycerol and glucogenic amino acids.
Why does gluconeogenesis matter if you are on the ketogenic diet?
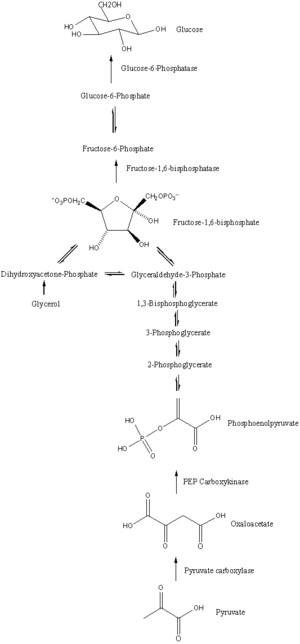 If you consume too much protein, your body converts it to glucose, it could spike insulin which would prevent weight loss.
If you consume too much protein, your body converts it to glucose, it could spike insulin which would prevent weight loss.
It could also knock you out of ketosis and if this glucose does not get used up immediately as energy, it will get stored in the body, resulting in weight gain.
However, you can keep your body from converting proteins to sugar by consuming much more fat than protein.
Also, if you exercise frequently, your body could use all that excess protein converted to glucose, which would temporarily knock you out of ketosis, but as soon as that glucose has been used up as energy, you would switch back to ketosis right away.
To learn more about what to eat to stay in ketosis, read What to eat on keto?
Find out how much protein you need on the ketogenic diet, read How to do a ketogenic diet?